Psoriasis Treatment
- Home
- Psoriasis
Panchhi Skin, Cosmetic & Hair Transplant Clinic
Psoriasis Treatment
At Panchhi Skin, Cosmetic & Hair Transplant Clinic, we offer advanced and customized care for psoriasis—a chronic skin condition that causes red, scaly patches. Our expert dermatologists use a combination of medical therapy, lifestyle guidance, and modern treatments to manage symptoms, reduce flare-ups, and improve skin health.
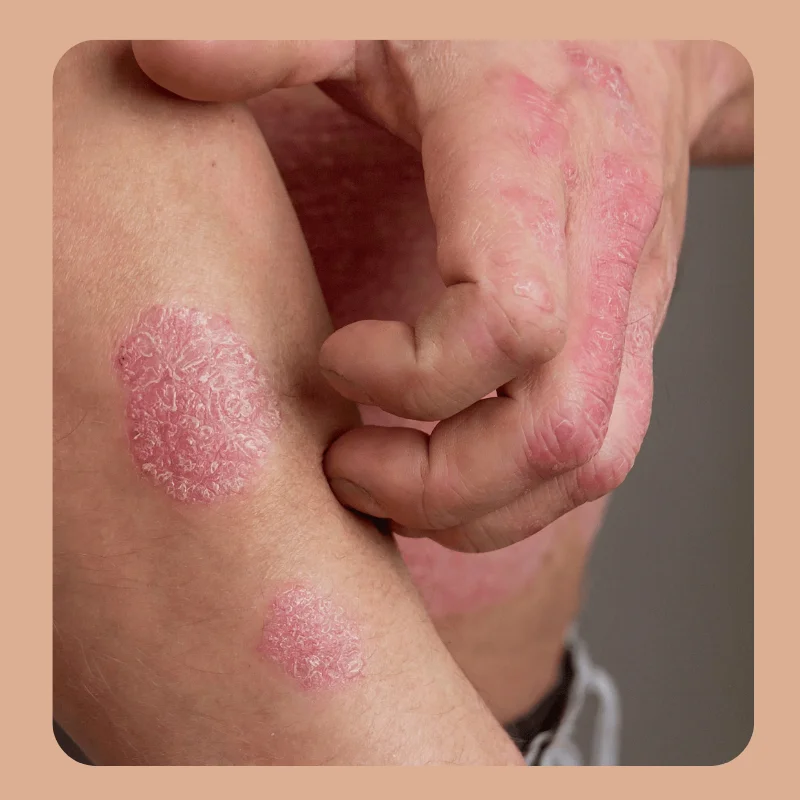
Psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune skin condition that leads to red, scaly, and itchy patches on the skin. At Panchhi Skin, Cosmetic & Hair Transplant Clinic, we provide comprehensive and personalized treatments—including topical medications, oral therapy, phototherapy, and lifestyle advice—to manage symptoms, reduce flare-ups, and improve skin appearance and comfort.
Panchhi Skin, Cosmetic & Hair Transplant Clinic
Frequently Asked Questions
Have questions about skin treatments or hair transplants? Our FAQ section covers everything you need to know.
Psoriasis is a non-contagious, chronic autoimmune condition that causes rapid skin cell buildup, resulting in red, thick, scaly patches.
It is caused by an overactive immune system and may be triggered by stress, infections, cold weather, certain medications, or skin injuries.
No, psoriasis is not contagious and cannot be spread from person to person.
Symptoms include red patches of skin with silvery scales, dryness, itching, cracking, and sometimes joint pain (psoriatic arthritis).
Treatments include topical creams, oral or injectable medications, phototherapy, and lifestyle modifications.
There is no permanent cure, but it can be effectively managed with the right treatment and care plan.
Results vary, but most patients notice improvement within a few weeks of starting treatment.
Manage stress, moisturize regularly, avoid known triggers, and follow your dermatologist’s treatment plan consistently.
